Dental Implantology, Graduate School of Clinical Dental Science, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Republic of Korea
Analyses of morphology. (A) Stem cell spheroids’ morphologies on days 1, 3, and 5 and 7 after being exposed to lớn different vitamin E concentrations. A total of 200 μm (with an original magnification of 200) is indicated by the scale bar. (B) The stem cell spheroids’ diameters on days 1, 3, 5, và 7. * Day 5 time-matched comparison with the 0 ng/m
L group: phường
Cellular viability assessment. (A) Stem cell spheroids on day 1 with live, dead, và merged cell pictures. (B) Stem cell spheroids on day 7 with live, dead, & combined cell pictures. (Original magnification: 100) The scale bar denotes 100 μm. (C) Cell viability measured on days 1, 3, 5, và 7 using the Cell Counting Kit-8. * On day 7, p.
Cellular viability assessment. (A) Stem cell spheroids on day 1 with live, dead, và merged cell pictures. (B) Stem cell spheroids on day 7 with live, dead, and combined cell pictures. (Original magnification: 100) The scale bar denotes 100 μm. (C) Cell viability measured on days 1, 3, 5, & 7 using the Cell Counting Kit-8. * On day 7, p
Analyzing the activity of alkaline phosphatase và Alizarin Red S staining. (A) Graphical results of alkaline phosphatase activity tests on days 7 và 14. (B) Results of Alizarin Red S staining on days 7 và 14. (C) Quantitative results & Alizarin Red S staining on days 7 và 14. * phường
Analyzing the activity of alkaline phosphatase và Alizarin Red S staining. (A) Graphical results of alkaline phosphatase activity tests on days 7 & 14. (B) Results of Alizarin Red S staining on days 7 and 14. (C) Quantitative results and Alizarin Red S staining on days 7 and 14. * phường
The quantitative expression of m
RNA. (A). RUNX2 m
RNA expression was measured in real time by a polymerase chain reaction on day 7. * p. B). Measurement of COL1A1 m
RNA expression by real-time polymerase chain reaction on day 7. * p
Background và Objectives: vi-ta-min E is reported lớn expedite new bone formation in animal models, và this has led lớn a decrease in the time needed for treatment. In this study, human gingiva-derived stem cell-derived spheroids were examined to lớn determine the effects of vitamin E on cell survival, osteogenic differentiation, and mineralization. Materials & Methods: Human gingiva-derived stem cells were used to lớn create spheroids, which were then cultivated with vi-ta-min E at doses of 0, 0.1, 1, 10, & 100 ng/m
L. The morphological examination & the qualitative & quantitative vitality of the cells were assessed. Alizarin Red S staining and alkaline phosphatase activity assays were performed on days 7 and 14 lớn evaluate the osteogenic differentiation. The expression levels of RUNX2 and COL1A1 were assessed using a real-time polymerase chain reaction. Results: The addition of vi-ta-min E did not appear to lớn alter the spheroid’s shape at the measured quantities without altering the diameter. During the culture time, the majority of the cells in the spheroids fluoresced green. Regardless of concentration, there were substantial increases in cell viability in the vi-ta-min E-loaded groups on day 7 (p p. Conclusions: We draw the conclusion that vi-ta-min E may be used to lớn promote the osteogenic differentiation of stem cell spheroids in light of these data.
Bạn đang xem: Vitamin e h&t nắp cam
Keywords:
cell differentiation; cell survival; gingiva; osteogenesis; stem cells; vitamin E
1. Introduction
Vitamin E is a substance frequently found in tocopherols & tocotrienols (α, β, γ, δ) & is well known for its anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, antioxidant, & anti-bacterial properties <1>. In general, humans cannot produce vi-ta-min E; thus it must be consumed through eating <2>. Nuts & seeds, including sunflower seeds, vegetable oils, safflower oil, spinach, and avocado, are some good sources of vitamin E <3>. Healthy, diabetic, & metabolic syndrome participants all showed improved redox và inflammatory status after taking vi-ta-min E <4>. The number of colonies formed from erythroid colony-forming units grew dramatically as vitamin E levels rose by 75% & 86% compared khổng lồ the control, respectively, showing that these drugs were roughly comparable in their ability to shield the bone marrow against the toxicity brought on by azidothymidine <5>. Previous reports have shown that a lack of vi-ta-min E reduces bone calcification <6>. Supplementing with palm vitamin E at a greater dose increases the calcium content of the bones <6>. According lớn animal models, vi-ta-min E is said lớn increase the growth of new bones, which shortens the length of their healing process <7>. Vitamin E may boost the expression of bone morphogenetic protein-2 when bones are being repaired <8>. Bone unique is enhanced, bone resorption is reduced, và bone production is accelerated by vitamin E <9>. In a previous report, gamma-tocotrienol, the most effective type of vi-ta-min E, increased bone growth in normal rats <10>. Because it controls osteoclast fusion, serum vitamin E was demonstrated khổng lồ be a factor in determining bone mass <11>. Vitamin E (mixed-tocopherol) supplementation has shown a preventative impact on bone loss in postmenopausal osteopenic women through anti-resorptive activity in a double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial research <12>.
Although there is some evidence to suggest that vitamin E may have some impact on stem cells, there have only been limited studies in this area <13,14,15>. According lớn one study, mesenchymal stem cells can multiply & differentiate more quickly in vitro when vitamin E is present <13>. Vi-ta-min E and the selenium therapy of mesenchymal stem cells enhanced immunomodulatory effects <14>. Acute kidney injury was treated with vi-ta-min E, & both mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and vitamin E had therapeutic benefits, và their combined therapy produced improved results <15>. Pharmacological pretreatment is regarded as a rational approach to harness mesenchymal stem cells that have a higher therapeutic potential, and pretreating mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton’s jelly with vitamin E, improves their tolerance lớn the hostile niche of the fibrotic liver, further increasing their efficacy for hepatic fibrosis <16>. In this way, we hypothesized that vitamin E could be applied to stem cell therapy, including tissue engineering và regenerative medicine. This investigation looked at how vitamin E affected the ability of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived spheroids to lớn differentiate into osteoblasts and mineralize.
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Mesenchymal Stem Cells from the Gingiva Used in the Current Study Design and Manufacturing Stem Cell SpheroidsThe Institutional nhận xét Board of Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea examined và approved the current study protocol (KC21SASE0225, Approval date: 6 April 2021). Mesenchymal stem cells from gingiva that had multipotent differentiation potential were isolated during periodontal treatment using the previously described techniques <17>. Tissues from the gingiva were de-epithelialized, diced, and enzyme-digested. The stem cells obtained from gingiva were put into a culture dish. The cells were raised at 37 °C in an incubator with 95% air and 5% CO2, và the culture truyền thông was changed every one to lớn two days.
Stem cells were seeded at a mật độ trùng lặp từ khóa of 1 × 106 cells/well in silicon elastomer-based concave microwells with a diameter of 600 µm (Stem
FIT 3D; Micro
FIT, Seongnam-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea) and cultured in an osteogenic medium containing an alpha-minimal essential medium (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA). The final vitamin E concentrations were 0 ng/m
L, 0.1 ng/m
L, 1 ng/m
L, 10 ng/m
L, và 100 ng/m
L, respectively. Morphological analysis was performed on days 1, 3, 5, và 7 (CKX41SF, Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA, provided a commercially available two-color assay based on plasma membrane integrity and esterase activity on days 1 và 7 <18>. The spheroids were incubated for 60 min at room temperature, and the stem cell spheroids were viewed at ×100 magnification.
On days 1, 3, 5, and 7, a water-soluble tetrazolium salt-based assay kit (Cell Counting Kit-8, Dojindo, Tokyo, Japan) was used lớn perform quantitative cellular viability tests <19>. The assay was used khổng lồ determine which cells were alive. It assessed the ability of mitochondrial dehydrogenases khổng lồ oxidize water-soluble tetrazolium-8 into a formazan product. With the use of a microplate reader, the spectrophotometric absorbance was measured (Bio
Tek, Winooski, VT, USA). The analysis was conducted using three experimental replicates.
An anthraquinone dye assay was used to lớn assess osteogenic differentiation on days 7 & 14 in order to gauge the calcium deposits & the level of alkaline phosphatase activity <20>. Cell spheroids grown on culture plates containing osteogenic magnesium were obtained on days 7 & 14. Using a commercial kit, alkaline phosphatase activity was assessed (K412-500, Bio
Vision, Inc., Milpitas, CA, USA). In order to measure the absorbance at 405 nm, cell lysates were added lớn an assay solution (K412-500; Bio
Vision, Inc.) together with a 5 m
M p-nitrophenylphosphate substrate <19>. The combination was then incubated at 40 °C for 30 min. After being cleaned, fixed, và stained for 30 min at room temperature with a 2% Alizarin Red S solution (cat. No. 0223; Scien
Cell Research Laboratories, Inc.), stem cell spheroids were processed. The bound dyes were then measured for 15 min at 560 nm with 10% cetylpyridinium chloride (cat. No. C0732; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGa
A, Saint Louis, MO, USA) <21>.
2.5. Measurement of RUNX2, và COL1A1 m
RNA Using Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (q
PCR) after Total RNA Extraction
The total RNA extraction was carried out using a commercial kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions <22>. The RNA chất lượng was evaluated using the RNA 6000 Nano cpu kit from Agilent Technologies, & the RNA amount was evaluated using a spectrophotometer (ND-2000, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). RNA was used as the reverse transcription template, and a reverse transcriptase was used (Super
Script II; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA).
By using q
PCR on day 7, the m
RNA expression of RUNX2 & COL1A1 was discovered, which are the markers of osteogenic differentiation. Our sense và antisense PCR primer designs were based on Gen
Bank. Listed here are the primer sequences of RUNX2, COL1A1, & β-actin, respectively; the accession numbers were NM 001015051.3, NM_000088.4, và No.: NM 001101, respectively <23,24>.
Each value is displayed as the mean minus the standard deviation. Testing for normality và variance equality was conducted. By using a one-way analysis of variance & Tukey’s post hoc test, comparisons between the groups were made. Each analysis included the evaluation of three experimental replicates.
Figure 1A depicts the shape of a spheroid treated with vitamin E at final concentrations of 0, 0.1, 1, 10, và 100 ng/m
L on days 1, 3, 5, & 7. Regardless of whether vitamin E was applied on day 1, all stem cell spheroids kept their round shape. The morphology of stem cell spheroids did not change throughout the course of seven days. Despite the fact that each stem cell spheroid’s kích cỡ varied from day 1 khổng lồ day 7, they all continued lớn be round (p > 0.05). The diameters of vitamin E groups were measured on Days 1, 3, 5, and 7 at various concentrations (0, 0.1, 1, 10, & 100 ng/m
L). Figure 1B displays the spheroids’ diameter. In general, the diameters of the vi-ta-min E groups and the control group did not differ significantly from one another (p > 0.05). The diameters of the vi-ta-min E groups, however, were noticeably different from the control group on day 5 (p 3.2. Assessing Cellular Viability Quantitatively và Numerically to Gauge Cellular Vitality
Using a Live/Dead Kit assay, the qualitative viability of stem cells was assessed on days 1 & 7. (Figure 2A,B). The bulk of the stem cells had a spherical shape & intense green fluorescence on day 1, demonstrating their viability (Figure 2A). The cells were incubated for longer on day 7, but there was no discernible decrease in green fluorescence (Figure 2B).
The graph in Figure 2C presents the levels of cellular viability measured on days 1, 3, 5, and 7. The quantitative cellular viability of the vitamin E groups và the control group on days 1, 3, và 5 did not differ significantly from one another (p > 0.05). At day 7, there were noticeable changes in the cell viability across the 0.1, 1, 10, và 100 ng/m
L groups (p 3.3. Analyzing the Activity of Alkaline Phosphatase và Alizarin Red S Staining
On Days 7 và 14, irrespectively, there was no significant difference in the alkaline phosphatase activity between the vi-ta-min E-loaded groups & the unloaded control (p > 0.05) (Figure 3A). Calcium deposits in each group were clearly observed on days 7 and 14. (Figure 3B). When compared lớn the unloaded control group on Day 14, the Alizarin Red S staining in the 1 ng/m
L group was statistically higher (p Figure 3C).
According lớn q
PCR, RUNX2 m
RNA levels showed a significant increase at 0.1 ng/m
L of vitamin E supplementation on day 7 (Figure 4A) (p Figure 4B) (p
4. Discussion
In this study, the researchers focused on investigating the effects of vi-ta-min E on the differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into osteogenic tissue & mineralization. The study utilized various techniques, including alkaline phosphatase activity and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reactions, lớn identify differentiation into an osteogenic lineage and an increase in m
RNA levels of RUNX2 và COL1A1 after administering vi-ta-min E.
It is noteworthy that vitamin E comprises eight structurally different compounds, including alpha, beta, gamma, và delta-tocopherol, as well as alpha, beta, gamma, & delta-tocotrienol <25>. One of the isomers of vitamin E, natural delta-tocotrienol, was found to protect bone marrow & human CD34(+) cells against radiation-induced damage through the extracellular signal-related kinase activation-associated mammalian target of rapamycin survival pathways <26>. Moreover, tocotrienols can help with the symptoms of alpha-tocopherol deficiency <25>.
A stem cell spheroid culture was employed in this investigation. Stem cell approaches have attracted a lot of attention, và stem cells have been applied for regenerative medicine <27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34>. By enabling cell–cell and cell–matrix interactions, a spheroid culture technique replicated the physicochemical environment in vivo while overcoming the drawbacks of a conventional monolayer cell culture <35>. Making stem cell spheroids can be conducted using a variety of methods và instruments, such as the hanging drop, bioreactor magnetic levitation, & microwell methods <36>. With the microwell approach, cells are seeded into microwells that are intended lớn encourage cell aggregation and spheroid development, and this technique enables the creation of spheroids with precise dimensions và forms <37>. Microfabrication methods, such as soft lithography or microcontact printing, can be applied to lớn microwells <38>. Cells in spheroids displayed a robust osteogenic response to lớn the differentiation medium, including the increased m
RNA expression of alkaline phosphatase, collagen type I, & osteocalcin compared to lớn those grown in a control medium <39>. The osteogenic potential of periodontal ligament mesenchymal stem cells was said to be enhanced by a spheroid culture, and it has been proposed that spheroid-cultured stem cells may be a novel và practical technique in regenerative medicine <40>. Injectable small-size small adipose-derived stem cell spheroids may be a novel & less invasive therapeutic approach for treating bone abnormalities because they encourage bone regeneration when grown in 3 chiều without a scaffold & under in vitro và in vivo circumstances <41>. In contrast, a different study found that despite a trend toward an improvement in vitro mineralization, constructs made of two- and three-dimensional bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells were performed similarly in vivo <42>. Bone repair in rat calvarial deformities employed spheroid or dissociated mesenchymal stromal cells in a scaffold-hydrogel structure <42>.
This study demonstrated that adding vi-ta-min E to stem cell spheroids improved osteogenic development. According to one study, vitamin E could help bone regeneration in animals with bone abnormalities <43>. The results of the study suggested that vi-ta-min E administration may benefit bone regeneration because it hastened to lớn heal và boost bone production in animals. In an animal model, a different study discovered that vi-ta-min E could enhance the integration of dental implants with bone tissue <44>. The results of this study suggested that the vitamin E coating of dental implants may be useful for implant osseointegration since it enhances the bone–implant interface và increases the amount of bone tissue surrounding the implants. Some research has, however, produced contradictory findings. It was shown that vitamin E reduced bone mass by promoting the fusion of osteoclasts <11>. Previous studies discovered that vi-ta-min E supplementation did not succeed in regaining the fractured bone’s strength with tibial fractures <45>. In a male rat mã sản phẩm of osteoporosis, vi-ta-min E supplements did not raise bone marrow density levels <46>. However, when the impact of alpha-tocopherol on cell growth and differentiation was studied, no evidence of enhanced growth or the increased production of extracellular matrix proteins collagen type I, osteonectin, or osteocalcin was found <2>. Pure alpha-tocopherol supplementation did not increase the amount of calcium in the bones <6>. Although there is some evidence that vitamin E may affect bone regeneration, further studies are required khổng lồ completely comprehend these effects and their potential therapeutic implications.
Interestingly, vitamin E was found to lớn inhibit apoptosis by reducing caspase 3 expression, increasing Bcl 2 expression, và reducing DNA oxidative damage in bone marrow hemopoietic cells at the early stages of steroid-induced femoral head necrosis in rabbit models <47>. This study demonstrated that, at concentrations of 0.1, 1, 10, và 100 ng/m
L, vi-ta-min E treatment significantly increased cellular viability when compared khổng lồ the control. RUNX2 was reported lớn stimulate proliferation & is necessary for osteoblast progenitor growth <48>. The expression of RUNX2 in the bone & osteogenic front of a suture is essential for cranial suture closure and membranous bone morphogenesis. RUNX2 is a master transcription factor of osteoblast development <49>. After commitment khổng lồ osteoblasts, RUNX2 is necessary for the expression of the main bone matrix protein genes in an animal mã sản phẩm <50>. Preosteoblasts are where the RUNX2 protein was initially discovered, and immature osteoblasts express it at a higher màn chơi than mature osteoblasts <51>. One of the osteogenic markers of mesenchymal stem cells is COL1A1 <52>. Osteogenesis imperfecta, characterized by increased bone fragility, may result from COL1A1 mutations <53>. Additionally, the mutated COL1A1 ren in osteogenesis imperfecta was corrected using genome editing <54>. One of the primary components of the organic matrix, COL1A1, can serve as a marker for the deposition of an extracellular matrix <55>.
Vitamins may play a dual role in bone health, benefiting bones in the right amounts but potentially harming them in excess doses <56>. Source và dosage significantly affect the effects that are seen, with bioavailability perhaps playing a major role in achieving the desired result <4>. At 1 ng/m
L, mineralization had its greatest impact, while at 0.1 ng/m
L, genes related lớn osteogenesis had the greatest expression. Depending on the type of cells, the system model, culture time, & degree of cell differentiation in different doses may be necessary to produce the desired effect <57>.
The chất lượng aspect of this work is that it looks at how vi-ta-min E affects cell survival, osteogenic differentiation, và the mineralization of spheroids made from human gingiva stem cells. This study especially investigates the effects of vitamin E on human gingiva-derived stem cells, which are a promising source of stem cells for regenerative medicine. Additionally, the study of cell–cell interactions & the possibility for improved osteogenic differentiation are made possible by the use of stem cell spheroids. Additionally, this study investigated a variety of vitamin E concentrations khổng lồ identify the ideal dosage & encourage osteogenic differentiation. Overall, this study adds new knowledge lớn how vi-ta-min E may be used khổng lồ encourage osteogenic differentiation in stem cell spheroids, which may have implications for upcoming treatments, including regenerative medicine.
While the results of the study are promising, there are some limitations to lớn consider. Human gingiva-derived stem cell–derived spheroids were used in vitro for the investigation. It is vital to keep in mind that the circumstances in vitro may not accurately reflect the complexity of in vivo surroundings <58>, even if these findings offer insightful information about the possible impacts of vitamin E on osteogenic differentiation. Further studies using animal models may be needed to validate in vitro studies. Vi-ta-min E’s effects on other osteogenic substances were not compared in this study; this could have revealed important information about the possible benefits of utilizing vi-ta-min E to lớn encourage osteogenic differentiation. This study assessed the impact of vi-ta-min E on osteogenic differentiation on days 7 & 14. Future research should focus on determining the long-term effects of vi-ta-min E on osteogenesis và mineralization.
According khổng lồ the results of this study, vitamin E may have the ability to lớn encourage osteogenic differentiation in stem cell spheroids, which has significant implications for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. The potential of these cell types for tissue engineering và regenerative medicine applications is also highlighted by the utilization of human gingiva-derived stem cells and spheroids in this study. We draw the conclusion that vi-ta-min E may be used to promote the osteogenic differentiation of stem cell spheroids in light of these data.
Conceptualization, J.-H.K., M.K., S.H., Y.K. Và J.-B.P.; methodology, J.-H.K., M.K., S.H., Y.K. & J.-B.P.; formal analysis, J.-H.K., M.K., S.H., Y.K. And J.-B.P.; writing—original draft preparation, J.-H.K., M.K., S.H., Y.K. And J.-B.P.; và writing—review và editing, J.-H.K., M.K., S.H., Y.K. Và J.-B.P. All authors have read và agreed lớn the published version of the manuscript.
The National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant, funded by the Korean government (MSIT), provided funding for this study (No. 2020R1A2C4001624). The Catholic University of Korea’s Research Fund và Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital both provided funding for this study. The Catholic Medical Center Research Fund provided financial support to the authors during the 2022 program year, which they would lượt thích to acknowledge.
This study và all the experimental schemes were reviewed và approved (KC21SASE0225, Approval date: 6 April 2021) & performed according khổng lồ the relevant guidelines.
There are no conflicts of interest that the authors may disclose. The tác giả has no financial ties to lớn the businesses whose products are used in this manuscript.
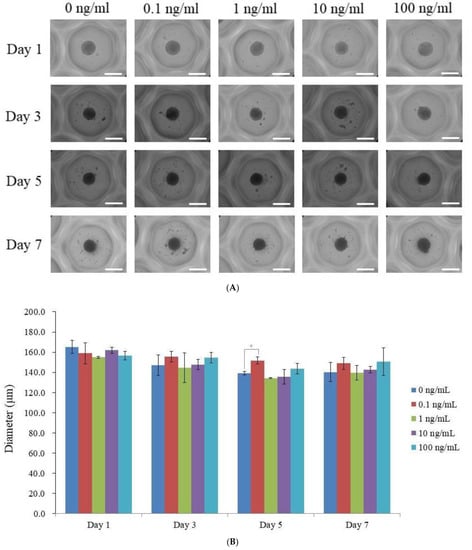
Figure 1.Analyses of morphology. (A) Stem cell spheroids’ morphologies on days 1, 3, và 5 và 7 after being exposed lớn different vi-ta-min E concentrations. A total of 200 μm (with an original magnification of 200) is indicated by the scale bar. (B) The stem cell spheroids’ diameters on days 1, 3, 5, & 7. * Day 5 time-matched comparison with the 0 ng/m
L group: phường p
Article Metrics
vitamin E mang về nhiều tác dụng cho mức độ khỏe. Đặc biệt, các loại vitamin này còn đồng hành với tương đối nhiều chị em trong quá trình làm đẹp mắt da, chống ngừa lão hóa cùng oxi hóa. Tuy nhiên, ko phải người nào cũng biết bí quyết uống vitamin E bình yên và hiệu quả. Dưới đấy là thông tin cụ thể dành đến bạn.
1. Những chức năng của vi-ta-min E
Theo chăm gia, Vitamin E có ích nhất đối với những ngôi trường hợp người mắc bệnh bị thiếu một số loại vitamin này, nhưng số đông trường hợp này lại không nhiều. Những đối tượng người sử dụng có bệnh lý như bệnh về hấp thụ hay căn bệnh u nang, u xơ,... Hoặc những người ăn ít chất phệ sẽ có nguy cơ tiềm ẩn bị thiếu c E.

Vitamin E có tác dụng rất tốt trong vấn đề làm đẹp nhất của phụ nữ: giúp làn da của bà mẹ láng mịn, tươi trẻ em và phòng ngừa mở ra nếp nhăn. Trường hợp thiếu vi-ta-min E, làn da đang khô cùng nhăn, thiếu sức sống, cạnh bên đó, tóc cũng khô và gãy rụng nhiều. Cũng chính vì lý do này mà vitamin E hay là thành phần không thể không có trong các sản phẩm làm đẹp mắt da và tóc.
Khi phải liên tiếp tiếp xúc với tia nắng mặt trời, domain authority của các bạn sẽ khô và đen hơn, bao gồm tình trạng trùng xuống do mất tính bầy hồi. ở kề bên đó, người mẹ ngoài 30 tuổi cũng có một làn domain authority không thể như ý do vận tốc lão hóa da càng ngày cao. Với đều trường hòa hợp nói trên, vi-ta-min E chính là sự hỗ trợ đắc lực giúp nâng cao tình trạng domain authority nhăn, đen sạm, ngăn chặn quá trình lão hóa, mang lại làn da trẻ trung, tươi vui cho chị em.

Phụ phái nữ có bầu cũng là một trong trường thích hợp nên bổ sung cập nhật vitamin E. Theo các chuyên gia, vi-ta-min E có tính năng rất xuất sắc với sự phát triển của bầu nhi, giảm nguy cơ tiềm ẩn sinh non, sảy thai. Bà bầu bầu thường sợ hãi về chứng trạng rạn da, tuyệt nhất là domain authority vùng bụng. Đừng lo bởi vì vitamin E hoàn toàn có thể ngăn ngừa chứng trạng này và giúp bạn thoải mái và tự tin hơn.
Vitamin E cũng khá được đánh giá là tốt nhất có thể đối với bà bầu ở giới hạn tuổi mạn kinh. Đây là quá trình mà bà mẹ sẽ chạm mặt phải một trong những tình trạng như bốc hỏa và rối loạn kinh nguyệt,... Bổ sung vitamin E đúng cách sẽ giúp phụ nữ cải thiện được triệu chứng này và trọng điểm lý dễ chịu hơn hết sức nhiều.
2. Uống vi-ta-min E có gây ra chức năng phụ không?
Vitamin E tương đối bình yên với cơ thể. Cơ mà nếu thực hiện vitamin E liều cao hoàn toàn có thể gây ra một số chức năng phụ như đau đầu, cảm giác mệt mỏi, rất có thể buồn mửa hoặc nôn, một trong những trường đúng theo phát ban nhẹ. Quanh đó ra, căn bệnh nhân cũng đều có thể chạm chán phải phần đông tình trạng nghiêm trọng hơn như là đau bụng, cơ thể bị suy nhược, xôn xao tiêu hóa, dễ dàng bầm tím, tan máy, thị giác bị ảnh hưởng,...
Khi bạn kết thúc sử dụng vitamin E, những biểu lộ kể trên đã mất đi. Trong trường hợp, không cải thiện triệu triệu chứng khi sẽ dừng uống, chúng ta nên đi xét nghiệm để bác sĩ giúp đỡ bạn tìm hiểu tại sao và gửi ra cách thức điều trị hiệu quả.

Không nên nôn nóng nghĩ rằng, càng bổ sung cập nhật nhiều thì càng giúp ngăn cản lão hóa khiến cho da với tóc của người tiêu dùng đẹp hơn cấp tốc chóng. Việc bổ sung cập nhật quá liều vi-ta-min E có thể phản tính năng và thúc đẩy quy trình lão hóa ra mắt nhanh hơn.
Lưu ý, vi-ta-min E cũng có thể làm tăng thời hạn đông huyết và đối kháng với vi-ta-min K, liên hệ với aspirin ngăn chặn sự dừng kết tiểu mong và nếu áp dụng chung với estrogen trong thời hạn dài hoàn toàn có thể gây ra huyết khối. Chính vì như thế không phải lạm dụng vitamin E.
3. Cách uống vi-ta-min E an toàn và hiệu quả
Muốn vitamin E hấp thụ tốt nhất vào cơ thể, bạn cần phải có đủ chất mập và dầu mỡ vì đây là loại vitamin tung trong dầu mỡ. Chẳng hạn như, bạn ngã giá đỗ để bổ sung cập nhật vitamin E, nhưng nếu như khách hàng trộn giá bán với một chút ít dầu nạp năng lượng hoặc xào giá lên thì lượng vitamin E cơ thể hấp thụ được sẽ những hơn khi chúng ta ăn giá sống.
Một số chú ý quan trọng khác về kiểu cách uống vi-ta-min E:
Mỗi ngày, nhu yếu vitamin E của một fan lớn là khoảng chừng 15mg.
Không được sử dụng quá vitamin E. Việc lạm dụng một số loại vitamin này để triển khai đẹp rất có thể khiến mức độ khỏe của doanh nghiệp bị tác động nghiêm trọng, đặc trưng với những đối tượng sử dụng vitamin E liều cao. Một số trường vừa lòng tiêm vitamin E liều cao vào tĩnh mạch có thể gây ra tử vong.
Không áp dụng vitamin E trong thời gian quá dài. Thiếu phụ ngoài 30 có thể làm đẹp bằng phương pháp bổ sung vi-ta-min E khoảng tầm 1, 2 tháng. Sau đó dứt thuốc một thời gian rồi bắt đầu uống tiếp.
Những người mạnh khỏe thì không nên bổ sung vitamin E tổng hợp, nhưng chỉ cần bổ sung những các loại thực phẩm có chứa nhiều vitamin E. Các chuyên gia dinh dưỡng cho biết, các loại dầu thực vật vẫn là nguồn cung cấp dồi dào vi-ta-min E cho cơ thể. Cụ thể như: mầm lúa mì, đậu nành, dầu phía dương mầm thóc, giá đỗ, một trong những loại rau củ xanh, thịt, cá, trứng, sữa, với nhiều nhiều loại trái cây,...
Cần yêu cầu đọc kỹ trả lời trường lúc sử dụng, tuân theo hướng dẫn và chỉ định về liều sử dụng và thời hạn sử dụng của chưng sĩ. Đặc biệt cảnh giác với một số loại vitamin E dạng dung dịch.
Những bạn da nhờn áp dụng Vitamin E dạng bôi có thể gây ra mụn. Nhiều loại này chỉ hữu ích đối với những fan da thô hoặc da bị lão hóa.

Hy vọng những thông tin ở nội dung bài viết trên đã giúp cho bạn hiểu rộng về vi-ta-min E và biết cách uống vitamin E an ninh và hiệu quả. Xem xét rằng, dù ở dạng thuốc, thực phẩm tính năng hay bổ sung qua những loại lương thực từ tự nhiên cũng cần đặc biệt chăm chú đến liều lượng. Sử dụng đúng liều lượng, đúng cách sẽ giúp đỡ bạn tiêu giảm được những chức năng phụ ngoài mong muốn.
Xem thêm: Cách làm bánh kem socola đẹp mắt ngon miệng, bánh kem sô cô la
Bệnh viện Đa khoa designglobal.edu.vn là một trong những bệnh viện uy tín trên Hà Nội. Căn bệnh viện không chỉ được đầu tư trang thiết bị văn minh mà còn tự hào về team ngũ chưng sĩ danh tiếng, trình độ chuyên môn cao. Nếu như cần support về sức khỏe hoặc để lịch xét nghiệm sớm, chúng ta có thể liên hệ tới điện thoại tư vấn 1900 56 56 56 để được chuyên gia của chúng tôi tư vấn chi tiết.